Types of Gynecological Cancers and How to Minimize Your Risk
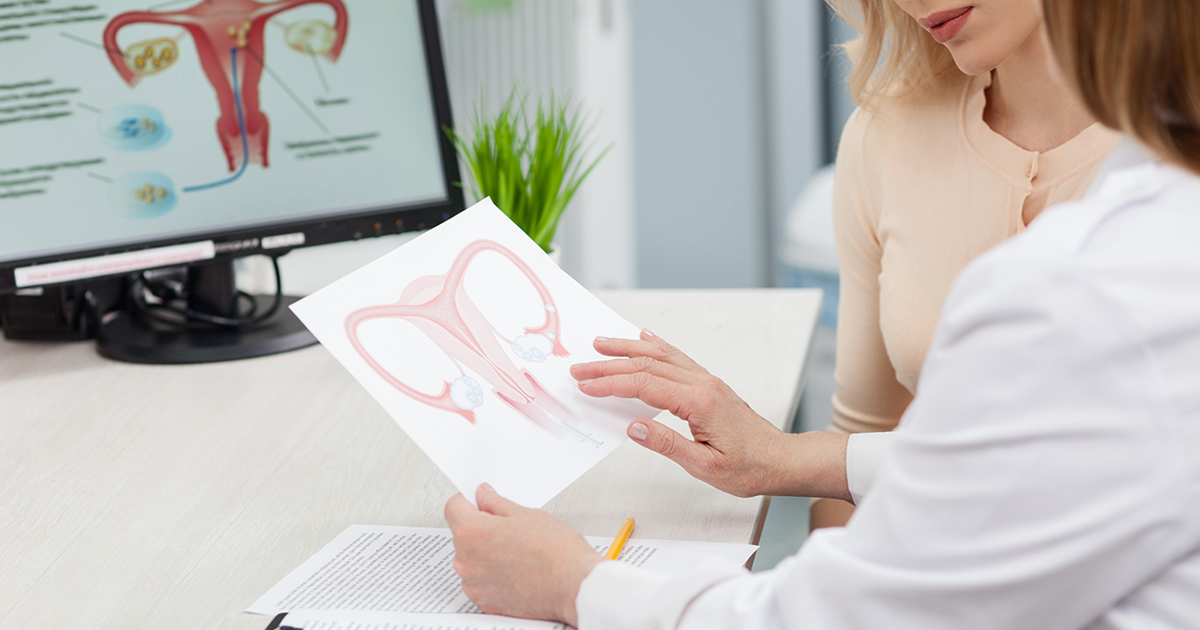

Gynecological cancer is cancerous growths that affect a woman’s reproductive organs. According to the CDC, the principal types of gynecological cancers are cervical, vaginal ovarian, uterine, and vulva. Only cervical cancer is easy to diagnose at an early stage. Here is why it is crucial to understand the risk factors and warning signs for gynecologic cancers Gilbert.
Types of gynecological cancer
Gynecological cancer refers to a cancerous growth that starts in the reproductive system. Scientists do not know the precise causes of most cancers. But they develop as a result of changes in the cell’s DNA.
The major types of gynecological cancer include:
- Uterine cancer: uterine cancer begins in the lining of the uterus called the endometrium. It claims the lives of 13,000 women every year. You may be susceptible to uterine cancer if you have excess weight or a family history. Women who have never given birth or started their menstrual cycle early are at an elevated risk.
- Ovarian cancer: ovarian cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers that affect the reproductive system. It starts from either of the ovaries that store eggs, on either side of the pelvis. The growth sometimes begins in the fallopian tube. The risk of ovarian cancer is higher in women over 50.
- Vaginal cancer: this is cancer that affects the vagina, a tube-like structure leading to the uterus. It causes pain and vaginal bleeding. The principal risk factors are advanced age and an HPV infection. Even though it is rare in the US, women over 60 are susceptible to vaginal cancer.
- Cervical cancer: This is a tumor that begins in the cervix, the narrow end of the uterus. The human papillomavirus (HPV) is the primary risk factor for HPV.
Gynecological cancer warning signs
Different gynecological cancers have varying symptoms. Since some cancers are not easy to diagnose with screening tests, understanding the warning signs is crucial for treatment.
If you have symptoms of gynecological cancer, it is always wise to consult your healthcare provider. Even when the symptoms are mild, you should schedule a diagnosis if they last more than two weeks.
Generally, the symptoms may include:
- Frequent urination could be a symptom of ovarian or vaginal cancer
- Abnormal discharge or bleeding is a common symptom of gynecological cancers
- Pelvic pain and a feeling of fullness could be signs of ovarian or uterine cancer.
- Itchiness or swelling on your vulva can be a symptom of vulvar or vaginal cancer
How to minimize your risk
The best way to prevent gynecological cancer is through screening tests. A pap smear test can detect cancerous cells emerging in the cervix.
HPV infections increase the risk of vulvar, vaginal, and cervical cancer. Women over 30 should undergo HPV screenings to reduce their risk.
An HPV vaccination can prevent infections but it does not treat existing cases of HPV. That is why it is advisable to be tested and vaccinated before getting an infection.
A review of your family history can help prevent some cancers. Your healthcare provider will provide counseling and testing after the diagnostic process.
To schedule a gynecological cancer appointment, contact Arizona Center for Cancer Care today.