Infection control: best practices for using personal protective equipment
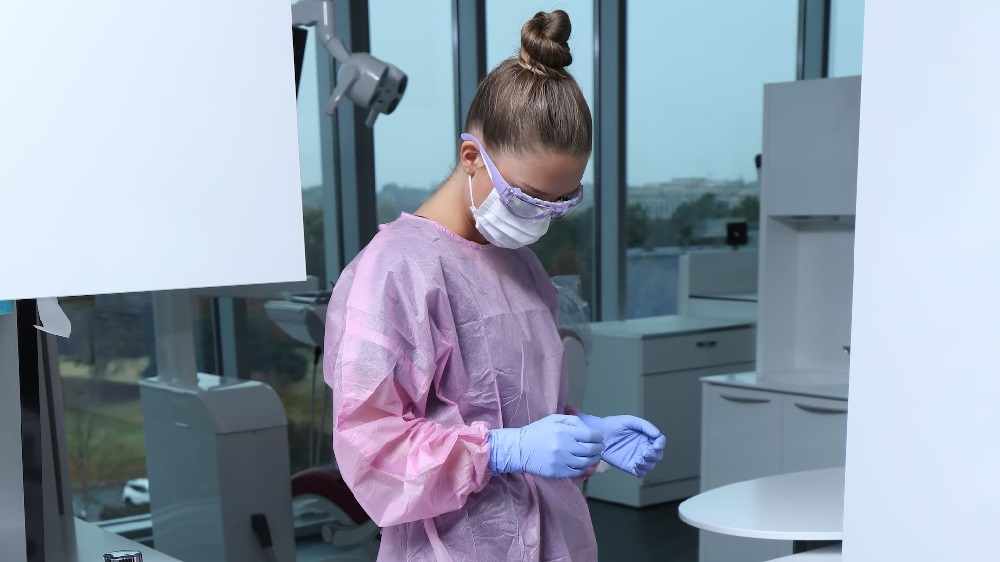

Personal protective equipment (ppe) is crucial in preventing the spread of infections in healthcare settings. Effective use of ppe not only protects healthcare workers but also minimizes the transmission of infectious agents to patients. This blog outlines best practices for using ppe, highlighting how to maximize protection through proper selection, use, and disposal.
Understanding different types of ppe
Ppe includes various items such as gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection, each designed to protect against specific hazards. Selecting the right type of ppe is essential depending on the clinical situation:
Gloves protect against contamination from blood and other bodily fluids.
Gowns shield the wearer from the spread of infectious agents.
Masks (including surgical masks and n95 respirators) prevent inhalation of infectious aerosols.
Face shields and goggles offer protection against splashes to the face and eyes.
Best practices for effective ppe use
To ensure ppe is effective in controlling infections, healthcare workers must adhere to these key practices:
Proper selection: choose ppe that is appropriate for the level of exposure anticipated. For example, gloves and gowns are necessary for direct patient contact, while n95 respirators should be reserved for procedures generating aerosols.
Correct donning and doffing: proper procedures for putting on and taking off ppe are crucial to prevent contamination. Always perform hand hygiene before donning ppe and after removing it. The recommended order for donning typically starts with gowns, followed by masks or respirators, goggles or face shields, and gloves. Doffing should occur in the reverse order, ensuring that potentially contaminated ppe does not touch clothing or skin.
Ensuring a proper fit: especially with masks and respirators, ensure a tight seal. A poor fit can compromise the protective barrier and increase the risk of infection.
Regular training and competency assessments: ongoing training on the correct use of ppe is essential. Healthcare workers should be regularly assessed for their proficiency in donning and doffing procedures.
Maintenance and disposal: single-use ppe should be disposed of properly after use to prevent contamination. Reusable ppe must be cleaned and maintained according to manufacturer instructions to ensure it remains effective.
Innovations in ppe
Recent advances have introduced more durable and user-friendly ppe options, improving safety and comfort for healthcare workers. For example, some gowns now feature materials that enhance breathability without compromising barrier protection. Innovations in mask design include features that reduce fogging of eyeglasses and enhance facial seal.
The role of ppe in infection control strategies
While ppe is a critical component of infection control, it must be part of a broader strategy that includes:
Environmental hygiene: regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces.
Administrative controls: policies and procedures that reduce exposure to inectious agents.
Engineering controls: physical modifications to the healthcare environment, such as improved ventilation systems, that help reduce the spread of infections.
Conclusion
Proper use of ppe is a key element of infection control in healthcare settings. By following these best practices, healthcare professionals can protect themselves and their patients from infectious diseases. Continued education, training, and adherence to protocols are vital to ensure the effectiveness of ppe and safeguard public health. As the healthcare industry evolves, ongoing improvements and innovations in ppe will continue to enhance the ability to manage and control infections effectively.