7 Causes Of Ear Pain You should Know About
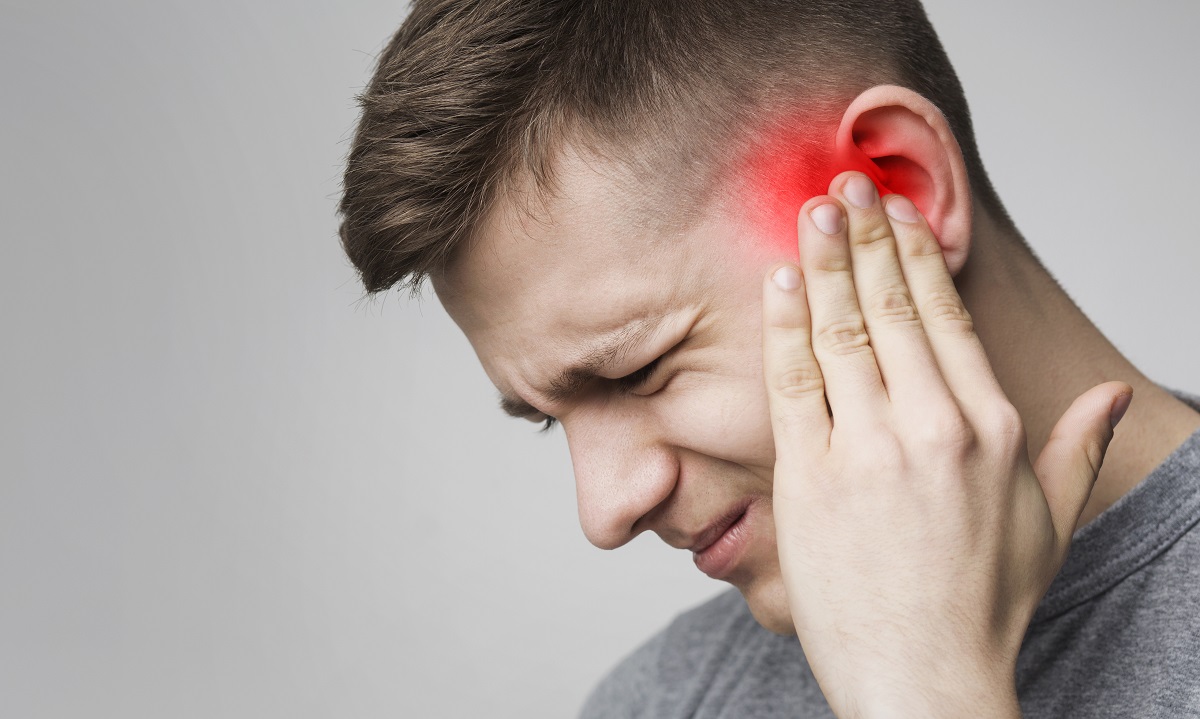
An earache might come from any of the three ear components. An earache might be in the outer, middle, or inner ear. Sinusitis, TMJ, or tooth infection can also cause ear pain. Your ear pain’s strength, location, and other symptoms (e.g., fever, dizziness) can help your doctor reach a diagnosis.
However, in some situations, imaging and blood tests may be required to rule out more serious causes of ear discomfort, such as mastoiditis or an ear tumor. Your ear pain treatment strategy will be based on your underlying diagnosis and may include a combination of therapy.
Causes of Ear Pain
Because there are numerous potential reasons for ear pain, it is most convenient to address primary diagnoses (which originate within the ear) and secondary diagnoses (which arise outside the ear) separately.
1-Otitis Media
Otitis media is a middle ear infection in which fluid and inflammatory tissue accumulate between the tympanic membrane and the inner ear’s oval window. In addition to moderate to severe throbbing pain deep in the ear, nasal congestion and coughing may precede the ear discomfort. Fever is another possibility.
Purulent (Poissy) ear discharge can occur if the eardrum ruptures due to pressure accumulation.
2-External Otitis
External otitis produces ear fullness, itching, and considerable ear pain when the earlobe is pulled. Yellowish or clear ear discharge, impaired hearing, and ear canal enlargement are possible symptoms. External otitis develops when water is stuck in the ear canal, hence the name “Swimmer’s Ear.”
Frequent usage of cotton swabs is another cause of external otitis. Inserting them into the ear canal can cause microscopic wounds that produce bacteria. External otitis can become necrotizing (malignant), spreading from the ear canal to the skull base. This issue is more common in senior diabetics.
3-Ear Wax Blockage
Earwax (cerumen) serves as a barrier between your ear canal and water, bacteria, and injury. However, sometimes too much earwax is produced, or the wax is pushed back too far (why healthcare providers recommend not using cotton swabs to clean out your ears).
If you have an earwax obstruction, you may experience ear discomfort, commonly described as a whole or congested feeling. Earwax blockage can also cause hearing loss and ringing in the ears.
3-Perichondritis
Perichondritis is an infection of the ear cartilage that causes discomfort, swelling, and redness on the skin’s surface. There may be a fever, and an abscess (a collection of pus) may form. Perichondritis can cause ear deformity (called cauliflower ear) if not treated, as the infection cuts off blood supply to the cartilage, causing it to die.
People with specific autoimmune disorders, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and those who have ear cartilage injuries are more susceptible to developing perichondritis (e.g., upper ear piercing, a burn, or harsh contact from sports).
Ear pain can be very disturbing and it usually doesn’t go away on its own. If you are experiencing increasing pain that lasts for more than two days, it would be better to consult an ENT specialist as soon as possible.
4-Sinusitis
Sinusitis is an infection or inflammation of the sinuses, which are hollow spaces behind the nose, behind the eyes, and in the cheeks and lower forehead, which are connected. Symptoms of sinusitis include:
- Ear pressure, discomfort, or a feeling of fullness
- Fever
- Congestion and discharge from the nose
- Toothache
- Headache
A viral infection or allergies cause most sinusitis cases; a bacterial infection causes just a tiny percentage of instances.
5-Meniere’s disease
Although the exact reason for the fluid retention in the inner ear is unknown, Meniere’s disease is caused by an excessive buildup of fluid in the inner ear. Additionally to the usual trifecta of symptoms—vertigo, ringing in the ears, and hearing loss—some persons with Meniere’s disease have ear pain or pressure in addition to the primary three symptoms.
6-Tumors
It’s rare, but an ear tumor, malignant or benign, can cause ear pain. For example, nasopharyngeal cancer can cause ear fullness, hearing loss, ringing in the ears, and recurrent ear infections.
In the ear, there are several types of noncancerous tumors or growths that can develop and cause pain, including:
- Cholesteatoma is a skin growth that grows in the middle ear that is not harmful.
- Acoustic Neuroma is a benign inner ear tumor that forms on the vestibular nerve, responsible for balance (eighth cranial nerve).
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
1-How can I relieve ear pain?
- A compress, either cool or heated. Soak a washcloth in cool or warm water, wring it out, and then place it over the sore ear.
- Using a heating pad: Place a warm, not hot, heating pad on your painful ear.
- Ear drops with pain medications are available over-the-counter.
2-Can COVID-19 affect your ear?
According to published case reports, acute hearing loss is an unusual sign of coronavirus onset. Several Iranian patients reported hearing loss in one ear as well as dizziness in a June 2020 report.
3-When to worry about ear pain?
If your symptoms do not improve within three days, you should consult your doctor right once. If your body temperature increases above 100.4 degrees and you have a fever, this could suggest a more severe infection. Ear infections are common, and they might eventually result in hearing loss.